INTRODUCTION
- Welcome to the future of aquatic exploration and environmental monitoring – the Automatic Water Sampling Boat. In an era where technology is revolutionizing our ability to understand and protect our planet's vital water bodies, this remarkable innovation stands at the forefront of scientific advancement.
- Imagine a sleek, intelligent vessel navigating through waterways with purpose and precision. Its mission: to gather invaluable samples that unlocks insights into water quality, ecosystem health, and environmental changes. This cutting-edge marvel has been meticulously designed to surpass the limitations of traditional sampling methods, offering unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and versatility.
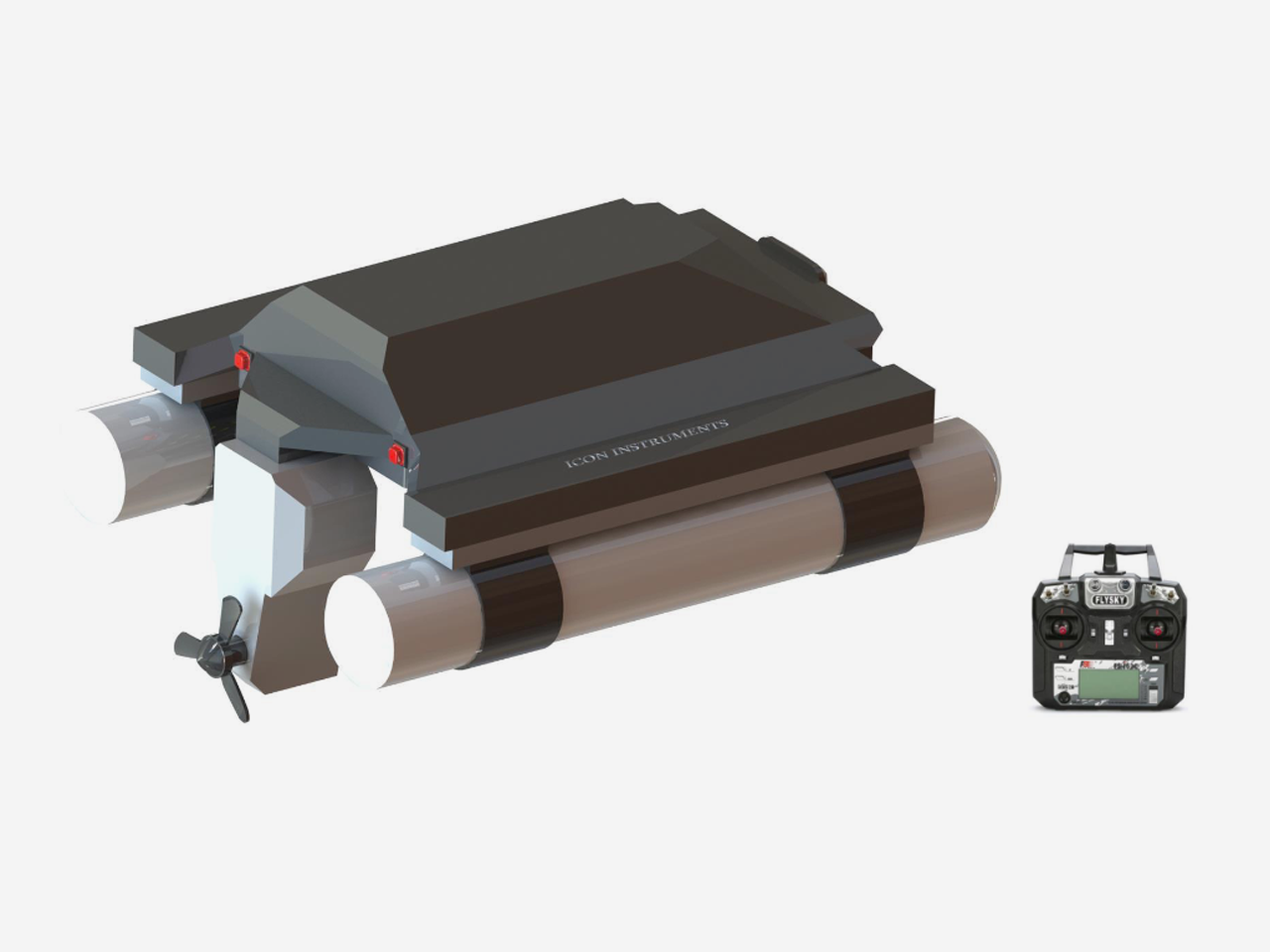
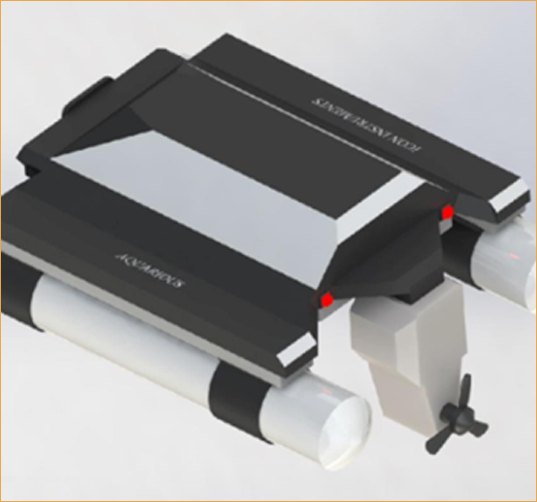
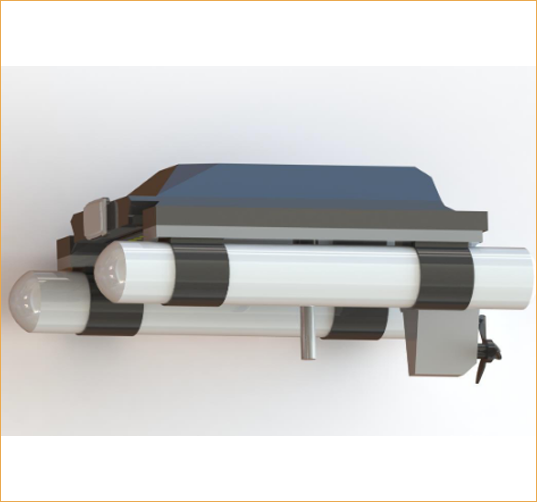
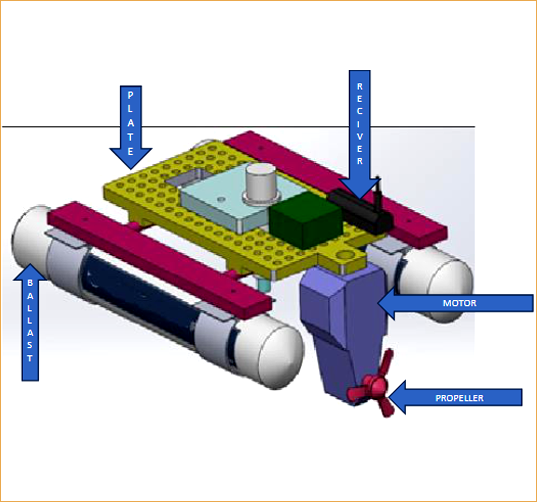
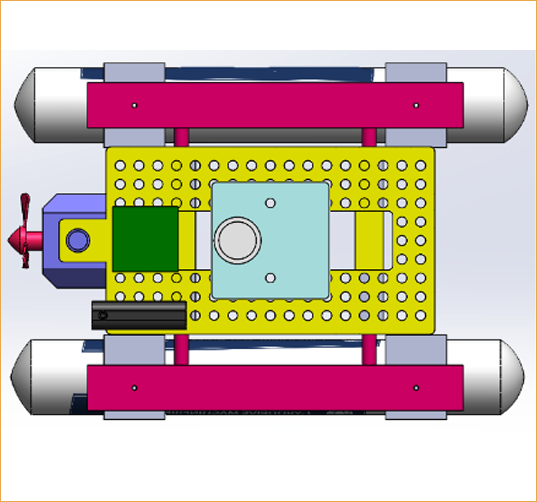
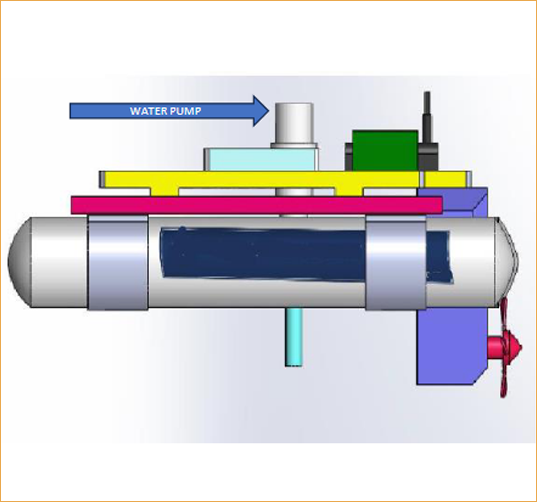
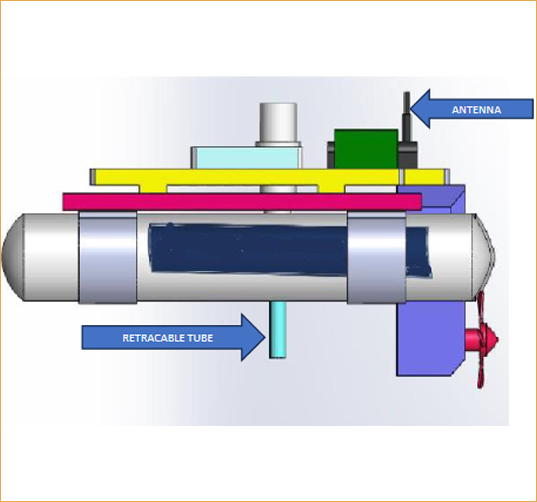
- Equipped with state-of-the-art technology which collect the water Sample from any specific location
- As we stand at the intersection of technology and environmental stewardship, the Automatic Water Sampling Boat embodies a promising future. It not only amplifies our understanding of aquatic ecosystems but also empowers us to take proactive steps towards preserving these invaluable resources.
TECHNICAL DETAILS
| Unit Mass | 10 kg |
| Transmitter | FS i6S 10 Ch (10 Channels |
| Receiver | FS iA10B (10 Channels |
| Battery | 12V 2200 mAh ( LiPo ) |
| Dimensions | 1000 mm x 830 mm x 750 mm (LBH) |
| Actuator | 300 mm 12V IP 65 |
| Pump | Gravity Suction (Valve Operated) |
| Speed | 10 km/h |
| Light | 1 Front 2 Back |
| Container Capacity | 1.5 liters |
| Range | 500 m LoS |
| Body | PVC and Carbon Fiber |
| Propeller Motor | 12V 100 W 300 rpm DC (2x) |
| Rudder Motor | DC Servo 20 W |
| Propeller | Molded ABS (Wheel Hub Mounted Paddle Type) |
| Weight Capacity | 24 kg |
| GPS Guidance | NEO 6M Module |
| Main Controller | Gyro DC V1 (12V 32 V Input) |